2-Wire vs 3-Wire vs 4-Wire RTD: Understanding PT100 & PT1000 Sensor Accuracy
Nov 25, 2025Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) are sensors that measure temperature by correlating the resistance of a sensing element with temperature.
When selecting an RTD sensor, the wiring configuration — 2 wire RTD, 3 wire RTD, or 4 wire RTD — is critical. The way each configuration handles lead-wire resistance can drastically affect measurement accuracy.

This is the simplest wiring configuration. Two wires connect the RTD element to the measuring device, which reads the total resistance of the circuit.
Diagram (2 wire RTD PT100 / PT1000): shows lead wire resistance adding to the sensor resistance and the basic temperature measurement principle.
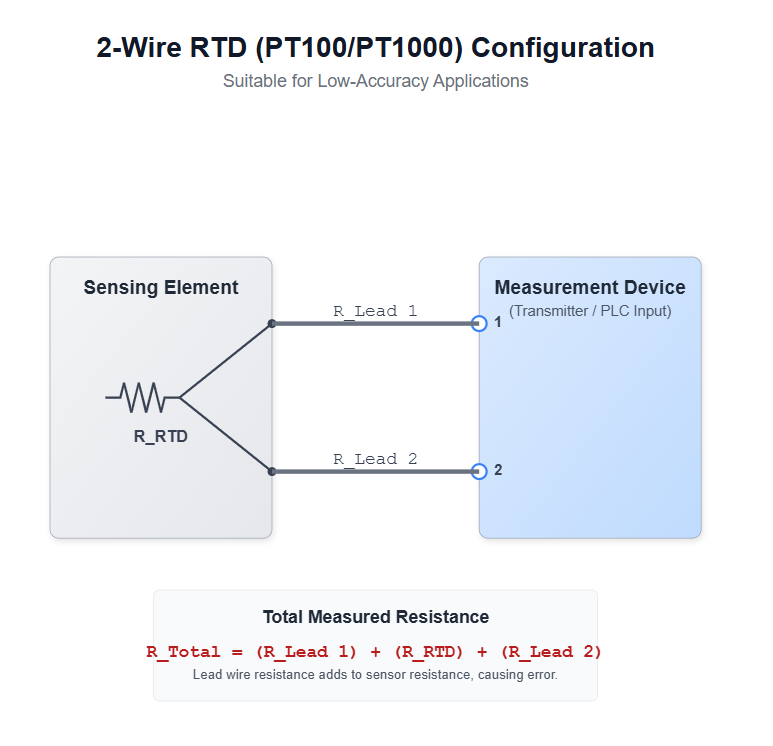
The lead-wire resistance adds to the sensor’s resistance — causing a higher than accurate temperature reading.
The longer the wires, the larger the error.
Therefore, 2 wire RTD is only suitable for applications with very short lead wires and where high precision is not required.
The 3 wire RTD configuration is the most widely used RTD wiring method in industrial settings. It offers a good balance between cost and measurement accuracy.
Diagram (3 wire RTD PT100 / PT1000): shows how equal lead-wire resistances are presumed and canceled out to improve measurement accuracy.
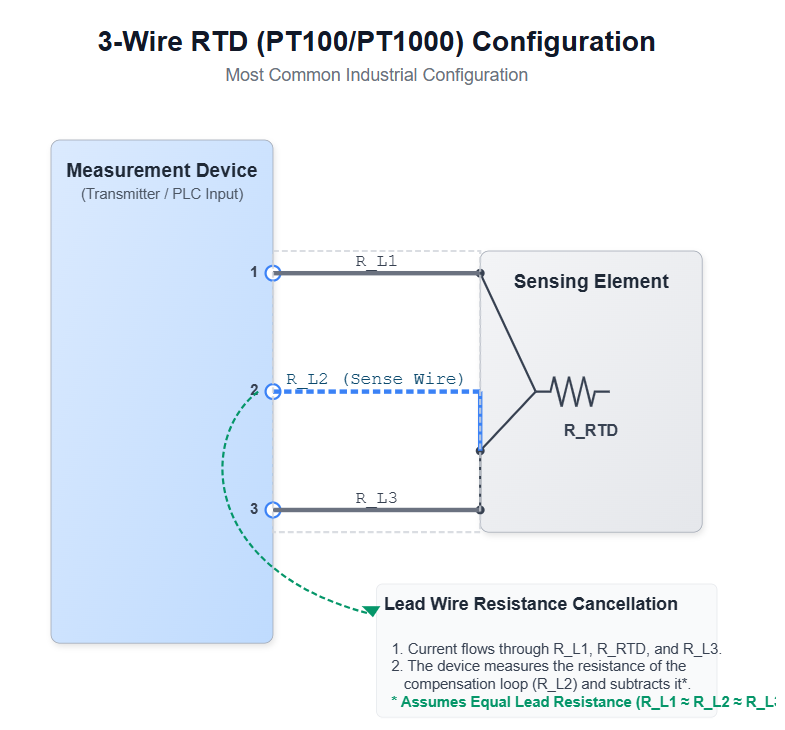
The 3-wire method uses a third wire to measure the resistance of a single lead wire and then compensate accordingly.
The measuring device sends a current through a loop consisting of the RTD element and two wires — measuring total loop resistance.
Using the third wire, it measures the resistance of one lead.
By subtracting twice that single-wire resistance from the total loop resistance, the lead-wire error can be effectively canceled out.
For the highest measurement accuracy, a 4 wire RTD configuration is the optimal choice. It effectively eliminates the influence of lead-wire resistance on temperature readings.
Diagram (4 wire RTD PT100 / PT1000, Kelvin connection): shows highest-precision temperature measurement with lead-wire resistance eliminated.
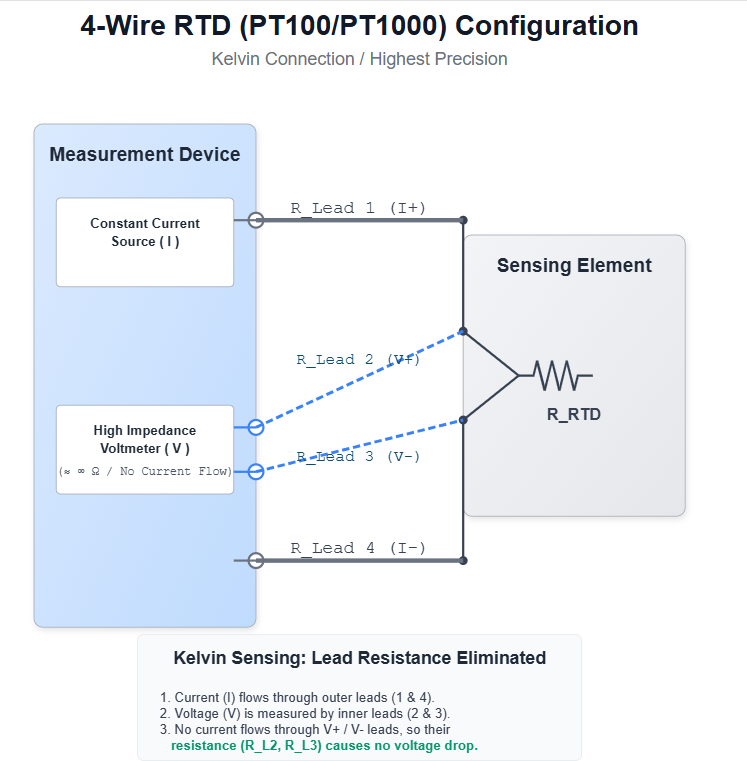
The 4-wire wiring employs a four-terminal (Kelvin) measurement method.
One pair of wires supplies a constant, precise current to the RTD element.
The other pair connects directly across the element to measure the voltage drop.
Since the voltmeter input has very high internal impedance, virtually no current flows through the voltage-sensing leads—and thus their resistance has negligible effect.
Using Ohm’s Law (R = V / I), the device calculates the RTD’s true resistance accurately — regardless of lead-wire length or condition.
| Scenario / Accuracy Requirement | Recommended RTD Configuration |
|---|---|
| Non-critical use, low precision requirement | 2-Wire RTD |
| Industrial systems, HVAC/automation, standard control systems | 3-Wire RTD (most common) |
| Laboratory, calibration, high-precision applications | 4-Wire RTD (highest accuracy) |
Use 2 wire RTD when precision is not critical and lead wires are short.
Use 3 wire RTD when you need a cost-effective, reasonably accurate solution for industrial and control-system environments.
Use 4 wire RTD when high accuracy is required, or when lead-wire length / environmental conditions may compromise measurement fidelity.
If you are unsure which wiring configuration suits your application, contact us — we will help you select the right RTD sensor.
What is the difference between 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire RTD sensors?
2 wire RTDs add lead-wire resistance, yielding the lowest measurement accuracy.
3 wire RTDs compensate for lead-wire resistance and are widely used in industrial systems.
4 wire RTDs completely eliminate lead-wire resistance effects and provide the highest accuracy.
Which RTD sensor is best for long cable installations?
The 4 wire RTD (PT100 / PT1000) is the best choice — because it removes lead-wire resistance errors, making it ideal for long-distance temperature sensing.
Is a 3-wire RTD accurate enough for manufacturing applications?
Yes. The 3 wire RTD is the standard configuration used in most plants. It offers good accuracy and stability for HVAC, automation, boiler systems, food processing, and industrial control.
Why choose PT100 or PT1000 RTD sensors over thermocouples?
RTD sensors (PT100 / PT1000) offer better stability, repeatability, and accuracy — especially in the –50 °C to 500 °C temperature range. Thermocouples are more suitable for extreme high-temperature environments (e.g. > 600 °C).
Does Focusens provide customized RTD sensors?
Yes. Focusens can supply customized PT100 / PT1000 RTD sensors — including 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire configurations — tailored according to lead-wire length, tolerance class, housing, and connector types.
Understanding the wiring configuration of your RTD sensor (2 wire RTD, 3 wire RTD, or 4 wire RTD) is essential — because the wiring choice directly affects measurement accuracy, especially when lead-wire length is significant or precision matters.
If you are not certain which configuration fits your needs, feel free to contact us. We’ll assist you in selecting and matching the RTD sensor best suited for your application.